Changing your MAC address can help to enhance your online privacy and allow you to bypass content restrictions. This is especially true if you use your device on public networks.
A change of MAC address can reset time-limited WiFi access and access control lists while making it harder to tie activity to your specific device. Additionally, if there are restrictions based on a device's IP address, changing the MAC address on your router can prompt your ISP to assign you a new one.
This blog will cover:
- What is a MAC address
- The two types of MAC addresses
- How to view your current MAC address
- How to change MAC address on Windows 10/11
- How to change MAC address in Linux
- Closing words & advice
Need a device to follow this tutorial? Sign up for BitLaunch and get a free trial of our Windows RDP and Linux VPS servers.
What is a MAC address?

A MAC address is a series of six pairs of numbers and letters embedded on a device's network interface controller (NIC). As MAC addresses are unique to each NIC, they are often used as a method to identify a device. Generally, they're used as a "name tag" for devices on a local network. They allow routers, switches, and other networked devices to recognize and communicate directly, without relying on higher-level protocols like IP addresses.
However, MAC addresses also enable targeted blocking and surveillance. For example, Edward Snowden revealed in 2013 that the NSA has a system that tracks the movements of mobile devices across a city by monitoring MAC addresses. MAC address tracking has also been used by traffic authorities and for targeted advertising.
The two types of MAC address
There are various ways to categorize MAC addresses (Unicast, Multicast, Broadcast etc.), but for this guide's purposes, the important distinction is:
- Universally Administered Addresses (UAAs): This is the MAC address assigned to the network interface out of the factory by the hardware manufacturer. Outside of specialist hardware, network chips do not allow the MAC address to be modified without changing the hardware itself.
- Locally Administered Addresses (LAA): An overridden, spoofed, or "software" MAC address. This can be presented to other network devices instead of the UAA.
We'll primarily focus on the latter here.
How to view your current MAC address
Before we start, you'll need to know how to check your MAC address so you can determine whether it has been modified successfully. Thankfully, the command for this is very similar across Windows and Linux, making it easy to remember.
In Windows:
Open command prompt and run:
ipconfig /all
Look for the entry reflecting the network adapter you'll be using. If you're on WiFi, this will be something like "Wireless LAN adapter WiFi". Ethernet should be "Ethernet adapter ethernet". The MAC address will be presented in the "Physical Address" row of the adapter.
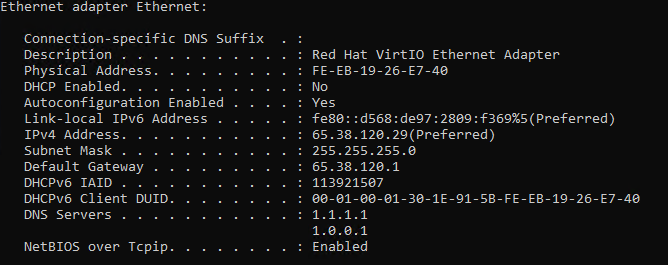
Note it down.
In Linux:
Open a terminal and run the below command just as you would with systemctl, iptables, or chown:
ifconfig
A list of all of your network adaptors and their MAC addresses will appear. On WiFi, you're probably looking for the one labelled wlan0. Your main Ethernet adaptor is probably eth0.
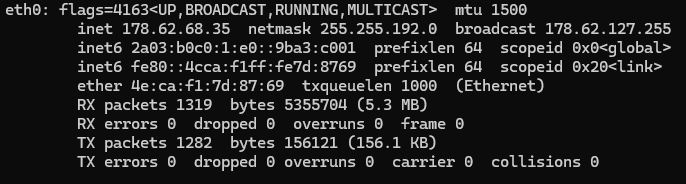
Note it down.
How to change a MAC address on Windows 10/11
There are a couple of ways to change your MAC address on Windows 10 and Windows 11. Some NICs let you change it directly in Device Manager, while others require you to use additional third-party software.
How to change MAC address on Windows using Device Manager
If your network adapter supports it, the easiest way to change your MAC address in Windows is in Device Manager:
- Press the Start button, type "Device Manager", and press Enter.
2. In Device Manager, expand the "Network adapters" column and find the WiFi or Ethernet adapter you are using. Right-click the adapter and choose "Properties".
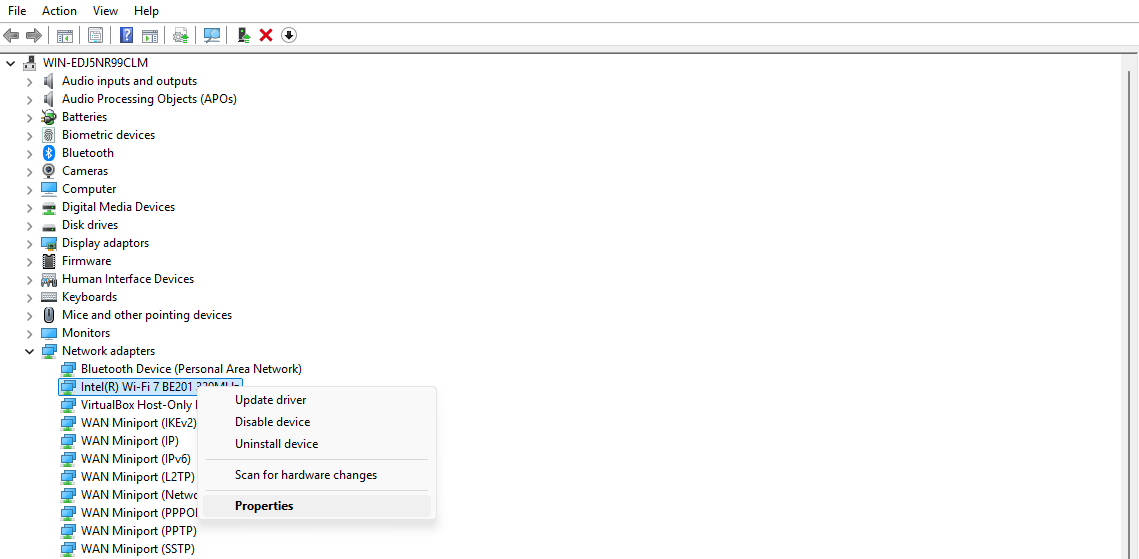
3. Open the "Advanced" tab and look for an entry related to MAC address in the property list. Change the Value to a valid MAC address (format 00-1A-2B-3C-4D-5E) and press "OK".
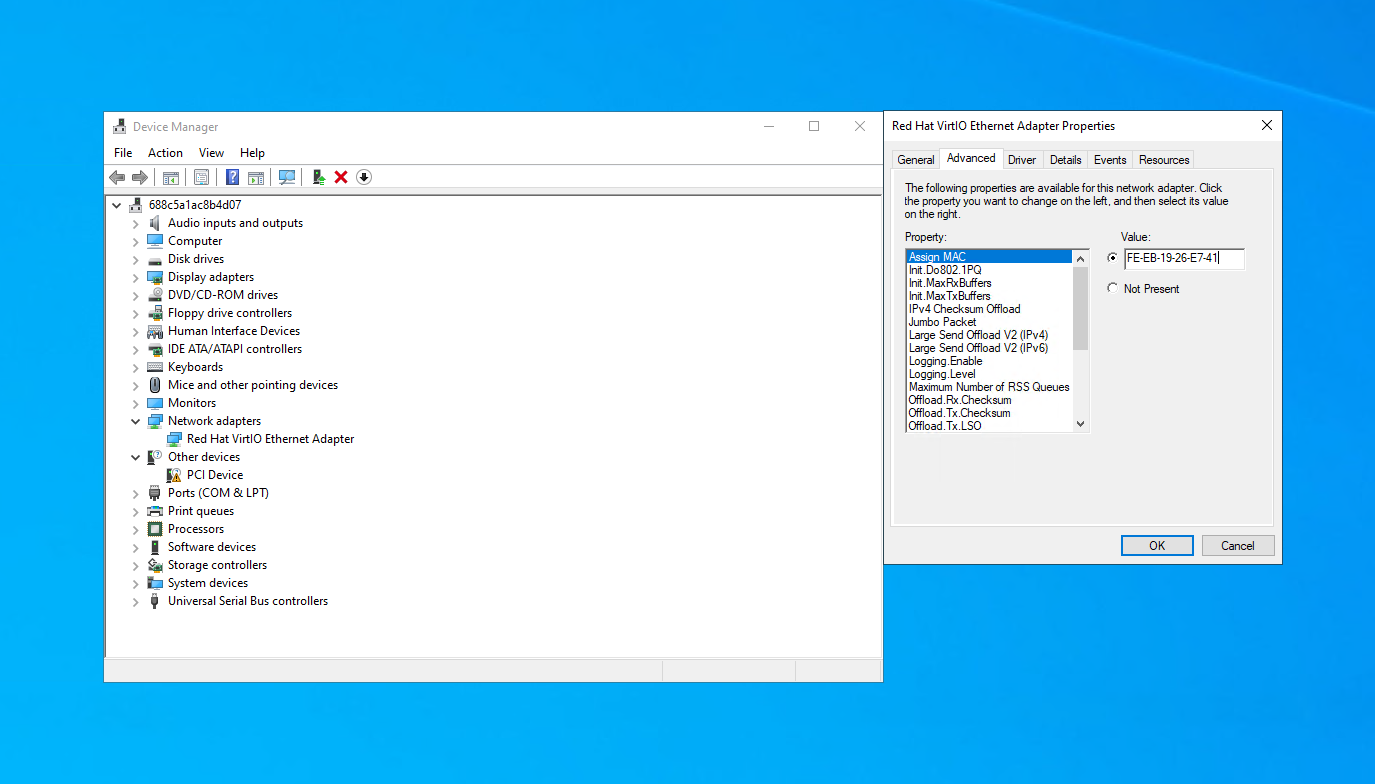
4. Check your MAC address has changed by running ipconfig /all once more.
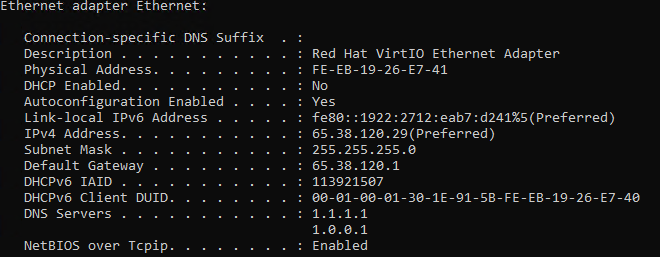
If you cannot load webpages after this change, restart your device. Your PC may need to obtain a new IP address from your router. You can alternatively try disabling and re-enabling the network adapter in Device Manager.
How to change MAC address on Windows using third-party software
There are several MAC address changer tools that let you change MAC address on PC. We can't offer a tutorial for each and every one, so we'll instead focus on one of the most popular, Technitium MAC address changer:
- Download, extract, and install Technitium MAC address changer.
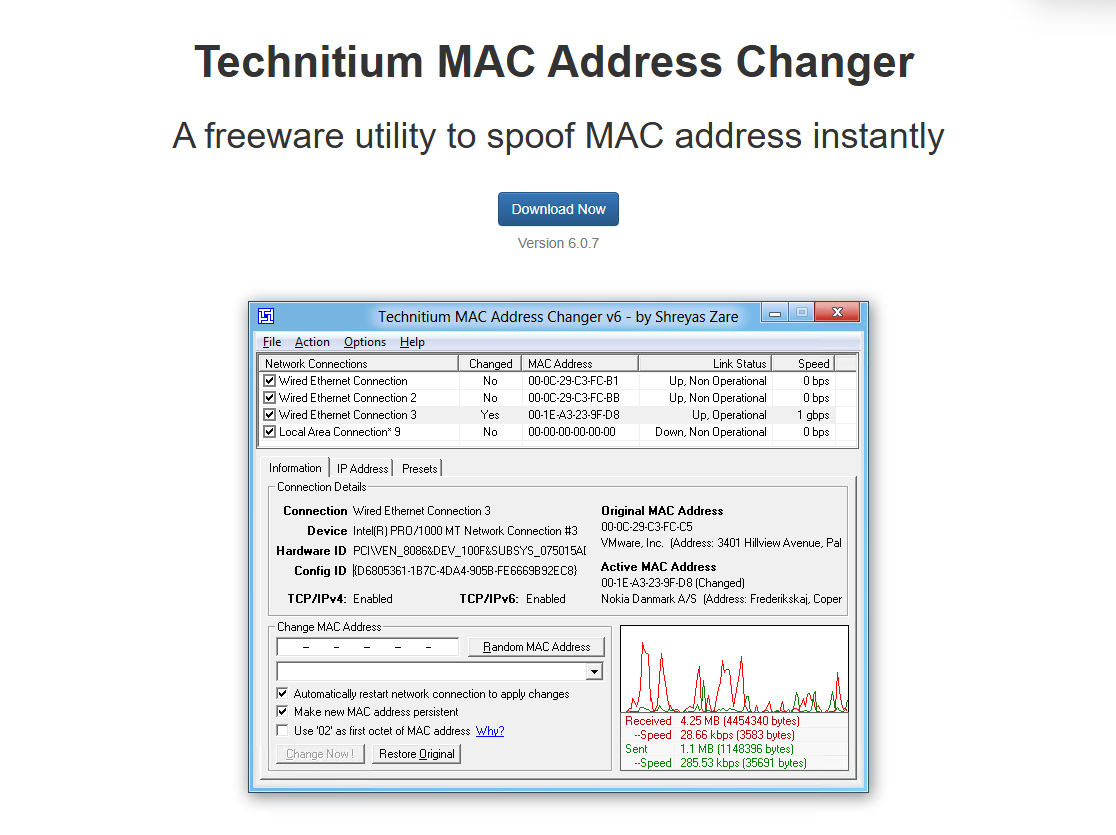
2. Select the adapter you would like to change the MAC address for in the top table and then press "Random MAC Address". On some adapters, you may need to tick "Use '02' as first octet" for the change to take.
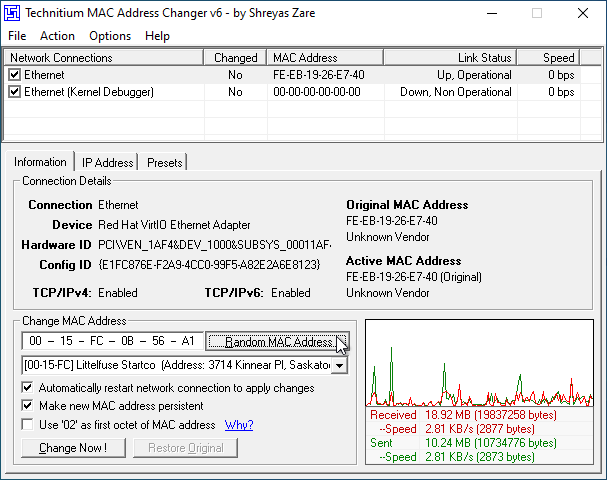
3. Press "Change Now!". Your new MAC address will now show in the "Information" section under "Active MAC Address".
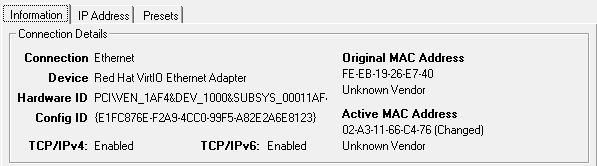
You can naturally also type a specific MAC address you want, and can restore your original if you run into any issues by using the "Restore Original" button.
How to change MAC address on Linux
Linux also has multiple options for changing your MAC address. The main choice is between a command-line utility like Macchanger or ip, and manually modifying your network config files. While the first option is a bit easier, you might not want to clog up your system or Linux RDP client with additional software, so we'll show you how to do both.
How to change MAC address temporarily on Linux with Macchanger
Macchanger supports most major Linux distros, including Ubuntu, from their default package manager. Here's how to use it step-by-step:
- Install Macchanger with your distros package manager (on Ubuntu,
sudo apt install macchanger).
2. Run the following command to change your MAC address to a random value:
macchanger -s <yourinterface0>
3. Replace <yourinterface0> with the network adapter you identified earlier using ifconfig. In most cases, this will be wlan0 or eth0.
4. Run ifconfig once more to verify that macchanger has successfully changed your MAC address.
You can alternatively assign a custom MAC address using the -m flag. For example:
sudo maccchanger -m 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E eth0
If you need to reset your MAC address to the original for any reason you can use the -p flag:
sudo macchanger -p eth0
How to change MAC address permanently on Linux via config file
Most or all distros allow you to change your MAC address by directly editing the config file for your interfaces. This will persist across reboots. The exact location and name of this config varies from distro to distro. We'll focus on Ubuntu here, but here are the locations for some of the most popular distros:
- Arch:
/etc/systemd/network/or/etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/ - CentOS:
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-* - Debian:
/etc/network/interfaces(or/etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/in newer setups) - Fedora:
/etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/ - Gentoo:
/etc/conf.d/net - Kali:
/etc/network/interfaces(or/etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/in newer setups) - openSUSE:
/etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-* - Ubuntu:
/etc/network/interfaces
Here are the instructions to change MAC address using the config file in Ubuntu:
- Type the following command and press Enter:
sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces
2. Search for the hwaddress under your adapter of choice (usually eth0 or wlan0)
3. Delete the hwaddress and replace it with your preferred one
4. Press Ctrl + O to save and Ctrl + X to exit.
For guidance on using nano, check out the below:

Closing words & advice
Changing your MAC address can help to avoid tracking, bypass filtering, and troubleshoot issues. On some devices, you may not even have to do so manually — both iOS and Android have "Randomised MAC" options for Wi-Fi networks. We recommend you check that this is toggled on.
Finally, a word of caution. Attackers can use MAC address spoofing for nefarious means, such as impersonating a legitimate device and gaining access to unauthorized networks. It's important to note that changing your MAC address for such purposes is usually illegal. Make sure you consider this both when changing your MAC address and when trusting devices on a network.
Sign up to BitLaunch and launch a Bitcoin VPS in Amsterdam, Bucharest, or the USA within minutes. Launch servers programmatically, or use our control panel to select from various regions and VPS providers.